1。 Metals: Metals are excellent thermal conductors due to their unique atomic structure. They have free electrons that can easily move and carry heat energy. Examples include copper, aluminum, silver, and gold.
2。 Some Nonmetals: While not as good as metals, some nonmetals can also conduct heat well. For example, diamond is an excellent thermal conductor due to its strong covalent bonds that allow heat energy to transfer efficiently.
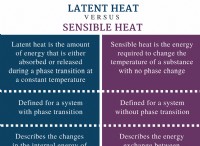
Factors affecting thermal conductivity:
* Atomic Structure: The arrangement of atoms and the presence of free electrons play a significant role.
* Bonding: Strong covalent bonds in materials like diamond allow for efficient heat transfer.
* 温度: Generally, thermal conductivity increases with temperature.
* 密度: Denser materials tend to be better thermal conductors.
* 不純物: Impurities can disrupt the flow of heat and decrease conductivity.
Examples of good thermal conductors:
* 銅: Used in cookware, heat sinks, and electrical wiring.
* アルミニウム: Used in building materials, aircraft, and packaging.
* 銀: Used in high-performance electronics and mirrors.
* ダイヤモンド: Used in industrial applications and jewelry.
In contrast, materials that are poor conductors of heat are called thermal insulators**. These materials prevent heat from flowing easily and are often used to trap heat or prevent heat loss. Examples include wood, plastic, rubber, and wool.